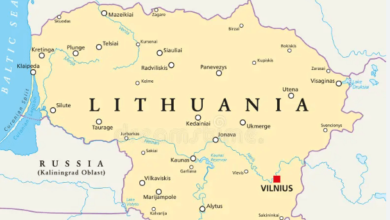
Blank:Uctz8h4duu8= Map
The ‘Blank:Uctz8h4duu8=’ map represents a significant advancement in the realm of geographical data visualization, particularly through its integration with Geographic Information Systems (GIS). This tool not only facilitates real-time data integration but also allows for a high degree of customization, making it suitable for diverse applications ranging from urban planning to environmental studies. As we explore its unique features and the implications of its use, one must consider how such tools are transforming our understanding of spatial relationships in contemporary contexts. What potential challenges and opportunities arise from this transformative approach?
Understanding the Map’s Concept
The concept of a blank map serves as a foundational tool in cartography, allowing for the representation of geographical data while emphasizing the underlying spatial relationships and potential information that can be integrated into its framework.
This versatility enables mapmakers to adapt the blank canvas for diverse applications, facilitating a clearer understanding of geographical phenomena and empowering users to explore and interpret spatial narratives independently.
See also: Beginner:7nbbaotekl8= Easy to Draw
Unique Features and Innovations
Innovative features of blank maps have evolved significantly, incorporating advanced technologies such as Geographic Information Systems (GIS) and interactive digital platforms that enhance data visualization and user engagement.
These innovations facilitate real-time data integration, customizable layers, and user-generated content, empowering individuals to tailor their mapping experience.
Consequently, blank maps serve not only as navigational tools but also as dynamic platforms for exploration and understanding.
Applications and Implications
Numerous applications of blank maps span various fields, including urban planning, environmental monitoring, and education, each utilizing the inherent flexibility and adaptability of these tools to meet specific spatial analysis needs.
In urban planning, blank maps facilitate zoning and infrastructure development.
In environmental monitoring, they enable the visualization of ecological changes.
In education, they serve as interactive resources for geographical literacy enhancement.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the ‘Blank:Uctz8h4duu8=’ map exemplifies the significant advancements in GIS technology, offering users a dynamic platform for spatial analysis and decision-making.
While some may question the complexity of such tools, the intuitive design and robust functionality facilitate user engagement and enhance understanding of geographical data.
By bridging the gap between data and actionable insights, this map serves as an essential resource across multiple sectors, underscoring its value in contemporary spatial analysis.